The RCT is a research methodology that involves randomly selecting subjects from a larger test group to receive an experimental product or service. Random allocation is a technique that chooses individuals for treatment groups and control groups entirely by chance with no regard to the will of researchers or patients condition and preference.

Three Versions Of Trial Design Within The Overall Rct Design Framework Download Scientific Diagram
After block size has been determined all possible balanced combinations of assignment within the block ie equal number for all groups within the block must be calculated.

. As the study is conducted the only expected difference between the control and experimental groups in a randomized controlled trial RCT is the outcome variable being studied1. Relational-Cultural theory RCT posits that we grow through and toward relationships throughout our lives and that growth-fostering relationships are the source of meaning and empowerment. Basically scientific errors of the past have taught us where we can go wrong drawing false conclusions from our research.
The purpose of this paper is to. Blocks are best used in smaller increments as researchers can more easily control balance. Randomized controlled trials RCT are known as the best method to prove causality in spite of various limitations.
The main intervention study design is the randomised controlled trial RCT. While they both rely on data the methodology differs such that a RCT is sniper-like in its precision and A. A randomized controlled trial is one of the best ways of keeping the bias of the researchers out of the data and making sure that a study gives the fairest representation of a drugs safety and.
After agreeing to participate patients are randomly allocated to one or more interventions or a control group and are followed until a finite date or the occurrence of one or more outcomes of interest. What is a randomized controlled trial RCT. Many criminologists doubt its applicability as a general theory of crime though much of this skepticism can be attributed to confusion and over-simplification of the model and the narrow range of variables and.
The intervention being tested is allocated to two or more study groups that are followed prospectively outcomes of interest are recorded and comparisons are made between intervention and control groups. An RCT is a study design that is generally used in experiments testing the effectiveness andor safety of one or more interventions. RCTs involve random assignment to groups and manipulation of the independent variable Schmidt Brown 2019 p.
I whether they use the new curriculum or not and ii who is teaching the class. In clinical research randomized controlled trials RCTs are the best way to study the safety and efficacy of new treatments. A randomized controlled trial RCT.
RCTs test a hypothesis whereas AB tests have more to do with rough assumptions. Blocks are then randomly chosen to determine the patients assignment into. 2 describe how the type of evidence needed varies according to whether the new test will be used as a replacement add-on or triage test and the intended benefits.
In practical terms this means that the pop-up message would be randomly assigned to be programmed in half of the computers the intervention condition but not in the other half the control condition. A pre-post clinical trialcross-over trial is one in which the subjects are first assigned to the treatment group and after a brief interval for cessation of residual effect of the drug are shifted into the placebo alternative group. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs surgical techniques medical devices diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments.
The Five Good Things Miller Stiver 1997 characterize these good relationships. A Randomized Controlled Trial is an experiment or study conducted in such a way that as many sources of bias as possible are removed from the process. Therefore if the study for example randomly assigns individual students to two classrooms that use the curriculum versus two classrooms that dont the study will not be able to distinguish the effect of the curriculum from the.
RCTs are designed to eliminate these major errors. For those familiar with the behavioral economics and nudge the response is probably obvious. A randomized controlled trial RCT is a type of quantitative experimental research study.
RCTs investigate the effects of an intervention or treatment on study participants. Excerpted from Transforming Community. An RCT is a prospective study following patients forward in time.
1 describe how a hypothetical RCT offers a useful conceptual framework to identify what types of comparative evidence are needed to evaluate a new test. A randomized controlled trial or randomized control trial. The randomised control trial RCT is a trial in which subjects are randomly assigned to one of two groups.
Rational choice theory RCT which is a prominent theoretical model in many fields of research can be applied to the study of crime. Participants are randomly assigned to either the intervention treated or. RCTs are used to answer patient-related questions and are required by governmental regulatory bodies as the basis for approval decisions.
RCT is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. The benefit of this approach is that it is the most rigorous method to determine whether a cause and effect relationship exists between a given service and the desired outcome. 3 The randomised controlled trial RCT is considered to provide the most reliable evidence on the effectiveness of interventions because the processes used during the conduct of an RCT minimise the risk of confounding factors influencing the results.
The pyramid shape is used to illustrate the increasing risk of bias inherent in study designs as one goes down the pyramid. A study design that randomly assigns participants into an experimental group or a control group. 1 zest 2 clarity 3 sense if worth 4.
Different ways to describe the effect Relative measures use division ratio of risk 015025 059 Relative risk 059 - 1 041 Expressed as a relative risk reduction Dexamethasone group had a 41 reduction in the risk of unfavorable outcome compared to the placebo group Absolute measures use subtraction difference in risk. One the experimental group receiving the intervention that is being tested and the other the comparison group or control receiving an alternative conventional treatment fig 1. RCT provides the.

Randomized Controlled Trials Chest

Randomized Controlled Trials Rcts Better Evaluation
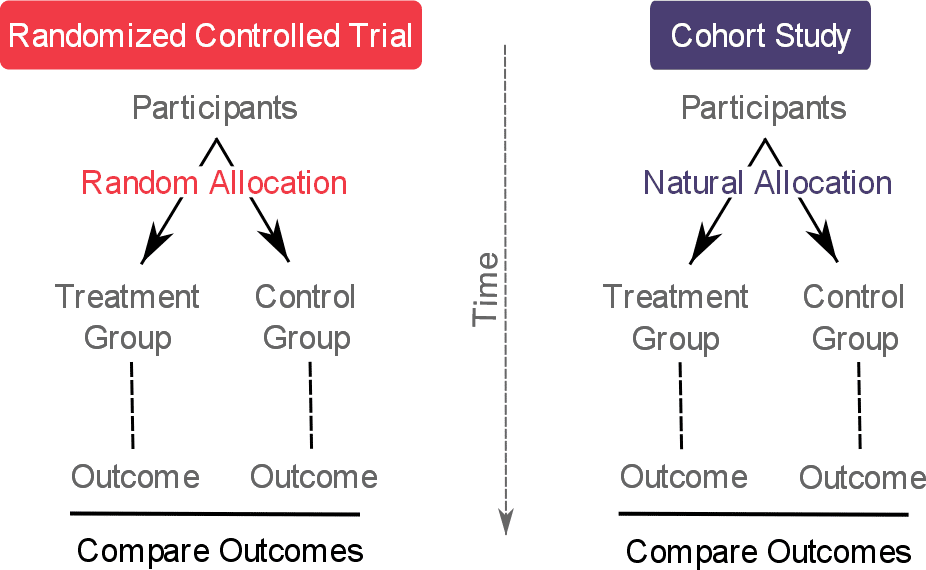
Cohort Vs Randomized Controlled Trials A Simple Explanation Quantifying Health
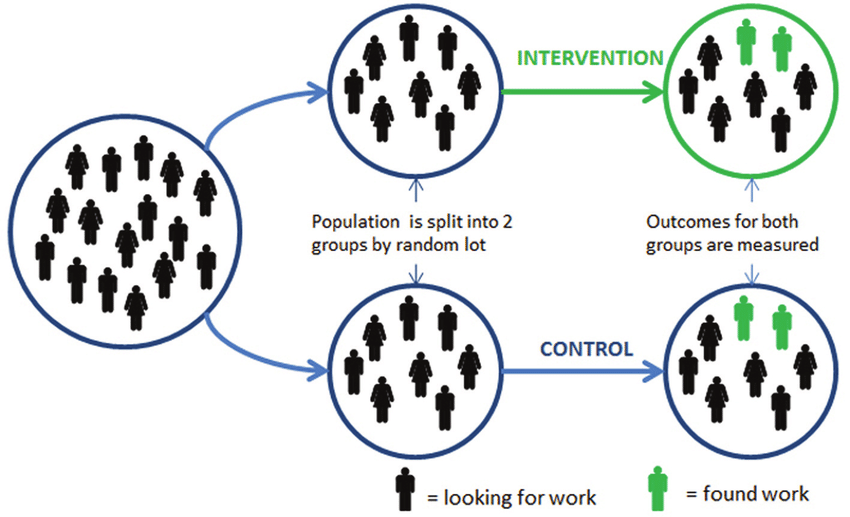
Illustration Of A Randomised Controlled Trial Rct To Test A New ʻback Download Scientific Diagram

0 Comments